3 Week3—Corrections
3.1 Summary
Here are several types of correction.
- Geometric correction: Used to correct geometric aberrations in satellite or aerial images caused by the curvature of the earth, terrain relief, tilt angle of the sensor etc.
- Atmospheric correction: Used to remove the negative effects of changes in light intensity and wavelength due to the interaction of light with particles and gases in the atmosphere as it passes through the atmosphere, which can affect the accuracy of images and data captured by satellite or aerial sensors.
- Orthorectification correction: Corrects for image distortions due to satellite imaging angles, inhomogeneities in the Earth’s surface (e.g., mountains or buildings), and the curvature of the Earth. Satellite imagery is thus converted into a realistic, accurately scaled map representation so that each pixel of the image corresponds precisely to a specific geographic location on the Earth’s surface.
(Radiometric Calibration: Ensure that images captured by satellite or aerial sensors are radiometrically accurate.)
3.2 Applications
Enhancement: Designed to improve the visual quality of an image, making features in the image more clearly recognizable.(E.g. Image Enhancement, Contrast Enhancement…)
3.2.1 Ratio
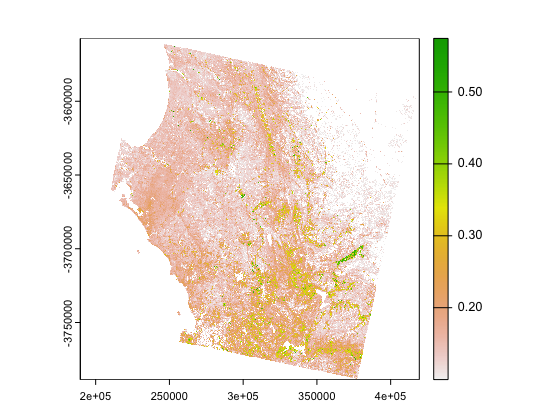
According to the practice, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) is primarily used to assess the density and health of surface vegetation. Based on the reflective properties of vegetation to solar radiation, especially in the red and near-infrared bands. Vegetation typically absorbs most of the red light (for photosynthesis) while reflecting more radiation in the near-infrared band.
My study area plot:
3.2.2 Texture
Texture analysis enhances the identifiability of objects or surface features in an image, especially in areas of single color or brightness. It describes the roughness, smoothness, and spatial distribution of these features on the surface of an object. By evaluating the relative position of pixels to each other and variations in brightness, texture analysis helps to extract more information about the surface.

My texture images looks very bad, so I use others. These images contains: the false color image on the left is probably going to be NIR, the image in the middle is a grayscale map of the red band, and the right is a grayscale map of the NIR band.
In this image we can see more clearly the farmland, houses, forests, etc. for further analysis.
3.2.3 PCA
PCA is a statistical method that transforms a set of possibly correlated variables into a set of linearly uncorrelated variables by orthogonal transformation, which is widely used for dimensionality reduction, data compression and feature extraction. It is used in remote sensing to improve contrast and remove unnecessary information.
3.3 Reflection
After this week’s class, I learned a lot about correction and enhancement, which in my understanding these are like makeup and Photoshop! When the camera takes a picture of our face and produces distortions, we can use Photoshop to adjust it to what it was supposed to look like, which is same as correction in remote sensing. When we feel that the photos are not in focus, we can adjust the contrast to make the photos look better, which is the same as the essence of enhancement in remote sensing. I wish I will more familiar with the code, I spend 6 hours to complete practical this week!
3.4 Reference
Warner, T. (2011). ‘Kernel-Based Texture in Remote Sensing Image Classification’. Geography Compass, 5 (10), pp. 781–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-8198.2011.00451.x.